Overview
The purpose of this article is to show how to effectively setup a cluster of machines in order to use Docker on them and to be able to optimize as much as possible the reource usage of the machines.
The aim is to create a proposal for building a clustered environment for a Continous Integration solution which allows to have isolated and reliable builds and avoid technology dependencies and overlappings.
Technology Overview
Mesos is an Apache project which has the aim to abstract the datacenters resources in a single pool of resources.
Apache Mesos abstracts CPU, memory, storage, and other compute resources away from machines (physical or virtual), enabling fault-tolerant and elastic distributed systems to easily be built and run effectively.
Have a look in the picture below to have a main idea of mesos architecture:
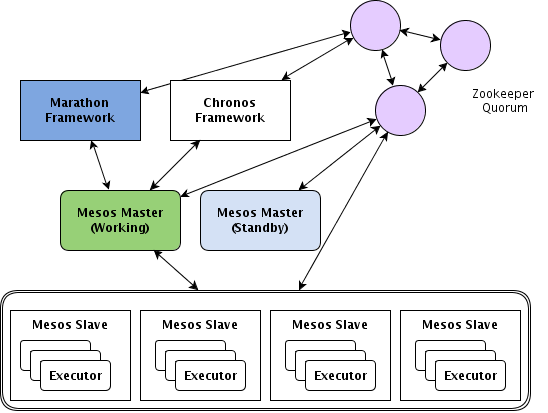
The main component of Mesos are:
- A framework is an application which is written directly against the Mesos REST APIs
- A frameworks connects to one of the master
- The master provides resources and frameworks can schedule tasks on this resources
- The slave consists on executor and they can run different types of executor
In the following image the mesos workflow is shown:
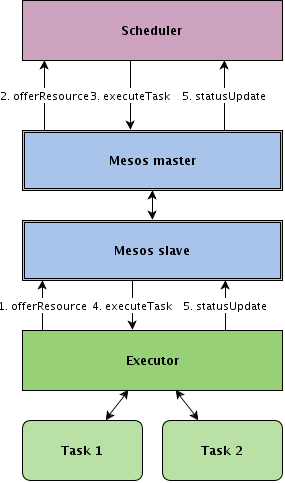
Mainly:
- The Mesos slave notices to primary Master that he has a total amount of resources available
- The Primary Master presentes the offer to the Framework (Marathon, Jenkins, …)
- The Framework accepts the offer useful for its needs
- The primary master executes the task from the Framework on the selected slave
Doing a POC: install mesos, marathon and jenkins on a single laptop
Installation:
I have chosen to install mesos using Mesosphere package, because it provides already usable services to run zookeeper, mesos-master, mesos-slave and marathon and chronos. I used an Ubuntu 14.04 machine with access to internet:
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv E56151BF
# set environment variable for identifying the distrubution and the codename
# In my case it will be 'ubuntu' and 'trusty'
DISTRO=$(lsb_release -is | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]')
CODENAME=$(lsb_release -cs)
echo "deb http://repos.mesosphere.io/${DISTRO} ${CODENAME} main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mesosphere.list
Once updated the ubuntu repository list run following commands:
sudo apt-get -y update
sudo apt-get install mesosphere
The mesospere installation installs all the listed services with startup automatically policies. I removed this feature simply creating overrides folder in the /etc/init folder:
sudo echo manual > /etc/init/chronos.override
sudo echo manual > /etc/init/zookeeper.override
sudo echo manual > /etc/init/marathon.override
sudo echo manual > /etc/init/mesos-master.override
sudo echo manual > /etc/init/mesos-slave.override
and now to start/stop services:
sudo service <service name> ( start | stop | restart )
Configuration:
All the configuration changes MUST be done with administrative privileges (i.e. using sudo)
Zookeper
The first step is to define a unique ID number, from 1 to 255, for each of your master servers. In my case the chosen value is 1. The value must be inserted in the following file:
/etc/zookeeper/conf/myid
Next step is to modify the zookeeper configuration file in order to ensure that the service can resolve the correct hostname (in my case is 127.0.0.1). The value must be inserted in the following file:
/etc/zookeeper/conf/zoo.cfg
After modification my partial file is like this:
server.1=127.0.0.1:2888:3888
Mesos
Please refer here for information about mesos settings. About environment paramentes they can be specified in the following file:
/etc/default/mesos
the content could be:
LOGS=/var/log/mesos
ULIMIT="-n 8192"
The value in that file are used both from mesos-master and mesos-slave services
About command line arguments they can be specified in the following folder:
/etc/mesos
In that case the folder mesos MUST contain one file for each command line argument and the filename MUST be exactly the name of the argument. The content of the file is the value of the argument.
Now let’s set the zookeeper url for the mesos services. Create a file named zk
/etc/mesos/zk
Fill it with the following content:
zk://127.0.0.1:2181/mesos
Mesos master
Also for the mesos-master service we have to set environment variables and commandline variables: About environment paramentes they can be specified in the following file:
/etc/default/mesos-master
the content could be:
PORT=5050
ZK=zk://127.0.0.1:2181/mesos
About command line arguments they can be specified in the following folder:
/etc/mesos-master
In that case the folder mesos-master MUST contain one file for each command line argument and the filename MUST be exactly the name of the argument. The content of the file is the value of the argument.
Now let’s set the quorum (for zookeeper) for the mesos-master services. Create a file named quorum
/etc/mesos-master/quorum
Fill it with the following content:
1
Next let’s set the work_dir for the mesos-master services. Create a file named work_dir
/etc/mesos-master/work_dir
Fill it with the following content:
/var/lib/mesos
Mesos slave
Also for the mesos-slave service we have to set environment variables and commandline variables: About environment paramentes they can be specified in the following file:
/etc/default/mesos-slave
the content could be:
MASTER=zk://127.0.0.1:2181/mesos
About command line arguments they can be specified in the following folder:
/etc/mesos-slave
In that case the folder mesos-slave MUST containe one file for each command line argument and the filename MUST be exactly the name of the argument. The content of the file is the value of the argument.
Now let’s set the ip for the mesos-slave services. Create a file named ip
/etc/mesos-slave/ip
Fill it with the following content:
127.0.0.1
Next let’s set the hostname for the mesos-slave services. Create a file named hostname
/etc/mesos-slave/hostname
Fill it with the following content:
127.0.0.1
Next let’s set the containerizers priority for the mesos-slave executors services. Create a file named containerizers
/etc/mesos-slave/containerizers
Fill it with the following content:
mesos
Finally let’s set the executor registration timeout for the mesos-slave services. Create a file named executor_registration_timeout
/etc/mesos-slave/executor_registration_timeout
Fill it with the following content:
5mins
Marathon
Marathon needs to run on the same master hosts. In order to be sure that everything is configured correctly I have set the hostname in the marathon settings. Be careful, because the Marathon folders settings are not created automatically:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/marathon/conf
Move to the generated folder and create a file called hostname
sudo echo 127.0.0.1 > /etc/marathon/conf/hostname
Now the zookeeper url needs to be specified in order to allow Marathon to gather information about scheduling and so on. Create a file called master
sudo cp /etc/mesos/zk > /etc/marathon/conf/master
Finally, let’s teach to Marathon to store its own state information in zookeeper. Create a file called zk
sudo cp /etc/marathon/conf/master /etc/marathon/conf/zk
Execution:
Start the services:
sudo service zookeeper start
sudo service mesos-master start
sudo service mesos-slave start
sudo service marathon start
Mesos interface can be reached at http://127.0.0.1:5050
Marathon interface can be reached at http://127.0.0.1:8080
Enjoy!
